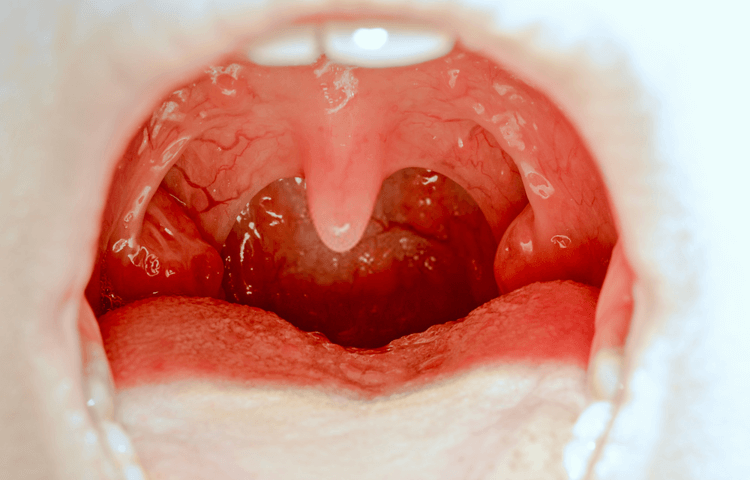
If you are unfortunate and have had your [palatine] tonsils removed or have reoccurring infections with your tonsils, this may just help …
The [group of*] tonsils provide:
- Protection against pathogens and toxins
- Lymphatic detox
- Excretion organ
- One of the greatest immune modulators
- Supporting the brains glymphatic system
This last point is massively overlooked, here’s why …
The glymphatic system is essential in mitigating risk against neuro-developmental disorders and degeneration, this ranges from Autism, Alzheimer’s through to some categories of depression.
This system clears the brain during sleep (mostly delta-wave sleep) of harmful proteins (such as amyloid-beta) and waste products by pumping the cerebral spinal fluid through the brain’s tissues. This flushes the waste into the body’s circulatory system in which it eventually reaches the liver where it can be eliminated.
This process is roughly 10 times more active during sleep as opposed to when awake. The brain also shrinks by around 60% of its original size to increase the efficiency of waste removal.
The removal of tonsils will also reduce the efficiency of the immune system, resulting in an increased chance for the development of food intolerances and possibly acting as a contributing factor towards autoimmune diseases (the severity of this risk is not currently quantifiable). If you have had your tonsils removed, there are several options you can do.
In my opinion, here are two of the most important:
- Massage the intracranial lymph (around the jaw and neck) to improve glymphatic circulation and possibly decrease neuroinflammation
- Ensure you have a good duration and quality of sleep (promoting delta wave sleep through binaural beats, gratitude logs or specific devices may help)
NERD TALK…
* The group of tonsils provide direct lymphatic drainage through the cribriform plate to Waldeyer’s Ring – this is a formation of lymphatic tissue situated in and around the:
- Pharyngeal tonsils (adenoids)
- Two tubal tonsils (posterior to Eustachian tu)
- Two palatine tonsils (this is what the tonsils is most commonly referred to)
- Lingual tonsil (base of tongue)
- Laryngeal tonsil (near the vocal cords in the larynx)